Seven indicators to distinguish economic cycle
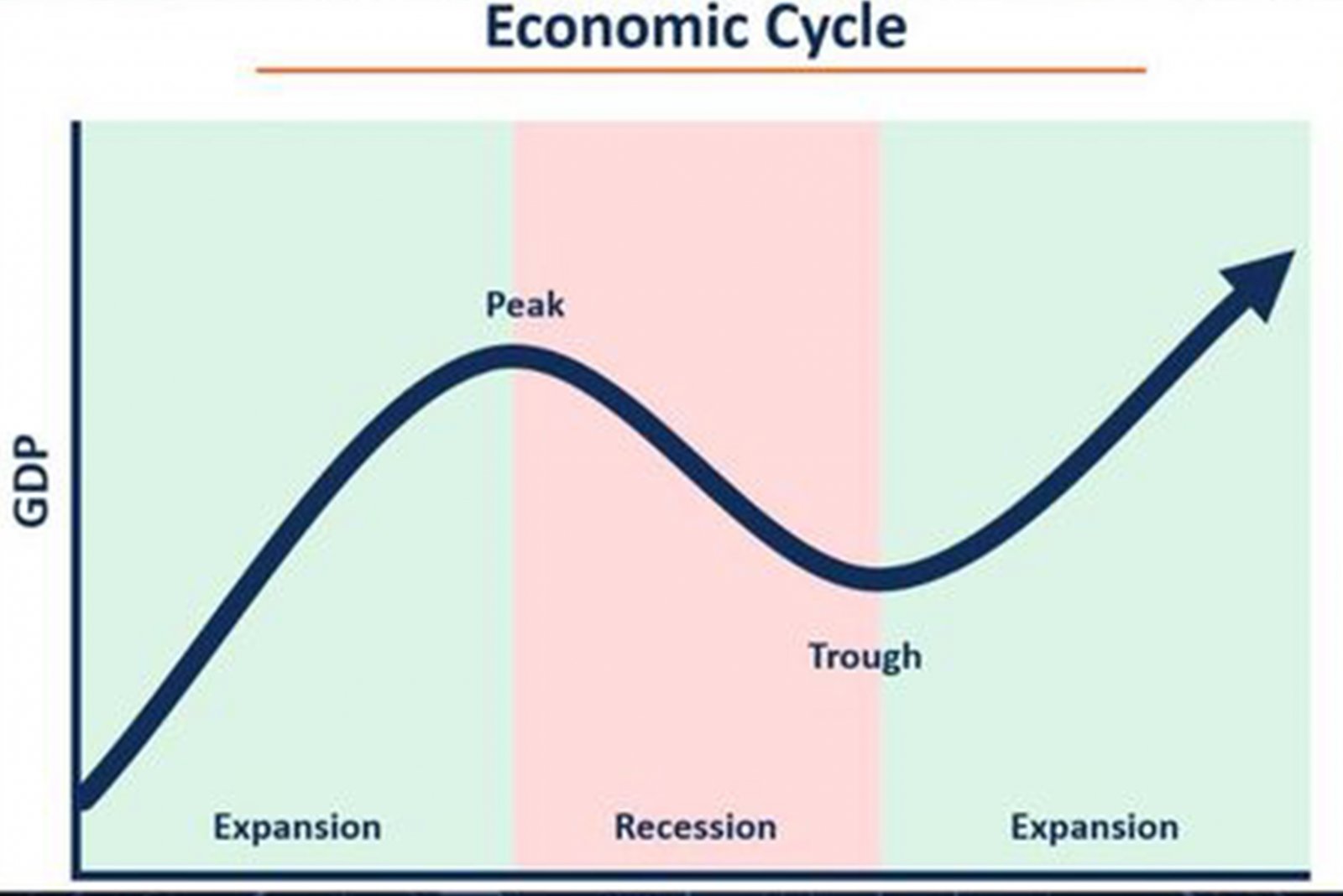
It is very important for investors to distinguish the economic cycle because different stages of the economic cycle have different effects on the investment market. The economic cycle is usually divided into four main stages: expansion, prosperity, contraction and recession. By observing seven economic indicators and market trends, we can identify the stage of the economy and formulate corresponding investment strategies.
GDP growth rate
Expansion stage: GDP continues to grow and the growth rate is accelerated. This stage is usually accompanied by an increase in production and consumption.
Prosperity stage: GDP growth rate reaches its peak and economic activity reaches its highest level.
Contraction stage: GDP growth rate began to decline and economic activity weakened.
Recession stage: GDP shows negative growth and economic activity is at a low point.
unemployment rate
Expansion stage: the unemployment rate is gradually decreasing, and more people have found jobs.
Prosperity stage: the unemployment rate is at a low level and the labor market is tight.
Contraction stage: the unemployment rate begins to rise, and enterprises reduce recruitment.
Recession stage: the unemployment rate has risen significantly and a large number of workers have lost their jobs.
CCI
Expansion stage: the index rises and consumers are optimistic about the future economic prospects.
Prosperity stage: the index reached its peak and consumer spending was strong.
Contraction stage: the index drops and consumers are worried about the future economic prospects.
Recession stage: the index is at a low level and consumers are pessimistic about the future economic prospects.
inflation rate
Expansion stage: gradually rising, increasing demand and rising prices.
Prosperity stage: When it reaches a higher level, the economy may overheat.
Contraction stage: it begins to decline, demand decreases and prices stabilize.
Recession stage: at a low level or even deflation.
interest rate
Expansion stage: the central bank may gradually raise interest rates to prevent the economy from overheating.
Prosperity stage: interest rates are at a high level to curb inflation and over-investment.
Contraction stage: the central bank may lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
Recession stage: interest rates are at a low level to promote consumption and investment.
Stock market performance
Expansion stage: the stock market performed well, the stock price rose and investors' confidence increased.
Prosperity stage: the stock market reaches its peak and the stock price is at a high level, which may lead to excessive speculation.
Contraction stage: poor performance of the stock market, falling stock prices, and declining investor confidence.
Recession stage: the stock market is at a low point, the stock price has fallen sharply, and investors are in a low mood.
industrial production index
Expansion stage: the index rises and industrial activities increase.
Prosperity stage: the index reached its peak and industrial production was active.
Contraction stage: the index drops and industrial activity weakens.
Recession stage: the index is at a low level and industrial activity is sluggish.
Previous Article Next Article


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Telegram
Telegram